Abstract
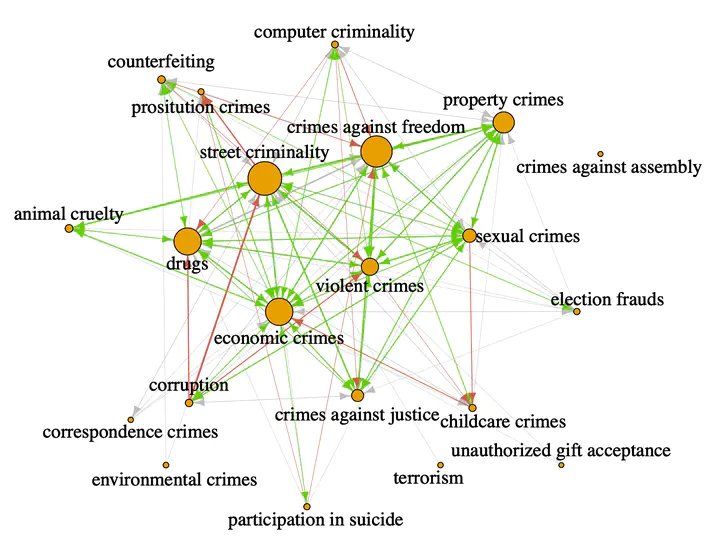
We use a comprehensive longitudinal dataset on criminal acts over five years in a European country to study specialization in criminal careers. We cluster crime categories by their relative co-occurrence within criminal careers, deriving a natural, data-based taxonomy of criminal specialization. Defining specialists as active criminals who stay within one category of offending behavior, we study their socio-demographic attributes, geographic range, and positions in their collaboration networks, relative to their generalist counterparts. In comparison to generalists, specialists tend to be older, more likely to be female, operate within a smaller geographic range, and collaborate in smaller, more tightly-knit local networks. We observe that specialists are more intensely embedded in criminal networks and find evidence that specialization indeed reflects division of labor and organization.